Planck's Quantum Theory
Planck's Quantum Theory: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Planck's Quantum Theory of Radiation, Quantum, Energy of a Quantum & Energy of a Photon etc.
Important Questions on Planck's Quantum Theory
The energies of two radiations are and , respectively. The relation between their wavelength i.e., will be:
The energy of second Bohr orbit of the hydrogen atom is hence the energy of fourth Bohr orbit would be :
The value of Planck’s constant is The velocity of light is Which value is closest to the wavelength in meters of a quantum of light with frequency of
Name the phenomenon which shows the quantum nature of electromagnetic radiation.
The frequency of radiation emitted, when an electron falls from to in a Hydrogen atom would be
(Given, ionisation energy of Hydrogen is and
If the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons ejected from a metal surface when it is irradiated with a radiation of frequency is then the threshold frequency of the metal is _______
Energy of an electron is given by . Calculate the wavelength of light required to excite an electron in a hydrogen atom from will be
The energy difference between the ground state of an atom and its excited state is , calculate the wavelength of the photon required to induce the transition.
Electromagnetic radiation of wavelength is just sufficient to ionize the atom of metal . The ionization energy of metal in is ______.
(Rounded off to the nearest integer)
Use:
What is the number of photons of light with a wavelength of that provide of energy?
When an electron present in ground state of -atom absorb a photon of energy How many times its wavelength increases.
Planck's constant second, velocity of light , the energy of photon of wave-length will be :
The energy of a photon is given as . The wavelength of the photon is :-
Planck’s constant has the units of
Which of the following transitions will have minimum wavelength?
mole of photons, each of frequency would have approximately a total energy of
mole of photons, each of frequency would have approximately a total energy of
If represents the Bohr radius, the de Broglie wavelength of the electron when it moves in the orbit after absorbing some definite amount of energy will be
If the ionization potential of the hydrogen atom in the ground state is, the longest wavelength of the radiation required to remove the electron from Bohr's first orbit will be approximately
Three energy levels and the wavelengths of the lines produced by transitions are shown in the figure below:
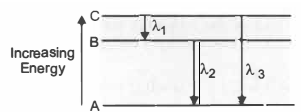
Which one of the following relationship is correct?
